mlplasmids FAQ
Published:
mlplasmids is an R package to predict if assembled short-read contigs from E. coli, K. pneunomiae or E. faecium originated from a plasmid or a chromosome. It uses species-specific machine learning classifiers which results in high precision and accuracy. mlplasmids can be used to predict the location of, for example, antibiotic resistance genes and the plasmidome content of a population of a bacterial species. The full description of mlplasmids is available as a preprint at bioRxiv.
FAQ
Why does it work?
The k-mer profiles of plasmids are different from the k-mer profiles of chromosomes of bacteria. While k-mer profiles of plasmids can be very diverse, the diversity observed in k-mer profiles of chromosomal sequences of a single species are usually limited, and can be used to differentiate species.
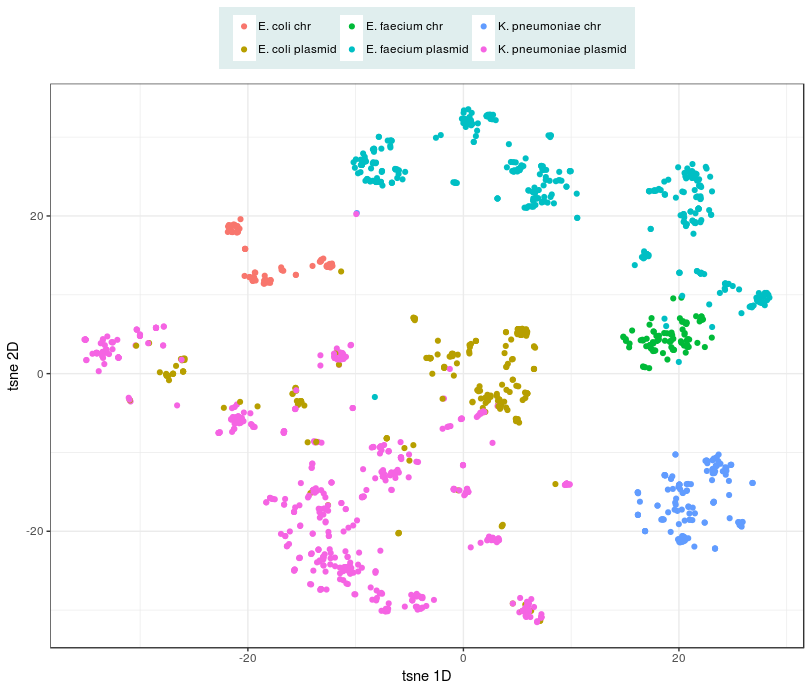 Computed mash distances between chromosome and plasmid sequences were clustered using t-sne.
Computed mash distances between chromosome and plasmid sequences were clustered using t-sne.
How does it work?
For each species, we trained machine-learning classifiers with contigs of known origin (plasmid or chromosome).
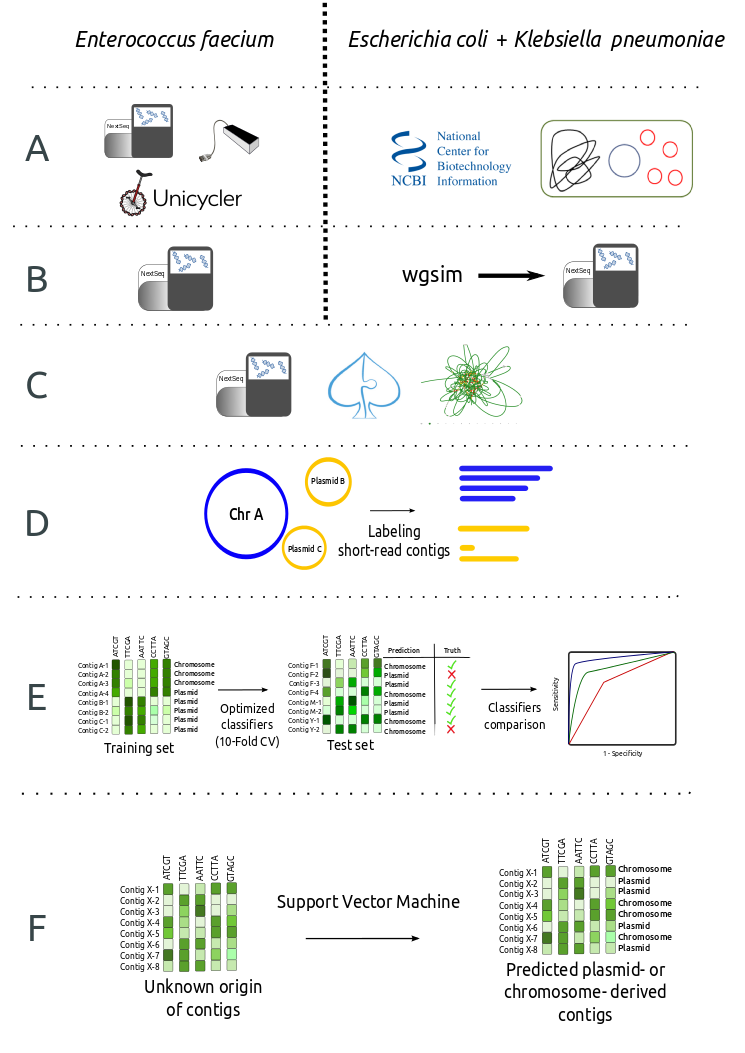
How does it compare to other plasmid prediction methods?
Favorably. However, I do not recommend its usage on metagenomes or other species than the ones currently included.
How can it be used?
To use mlplasmids with single genomes
Use the webserver
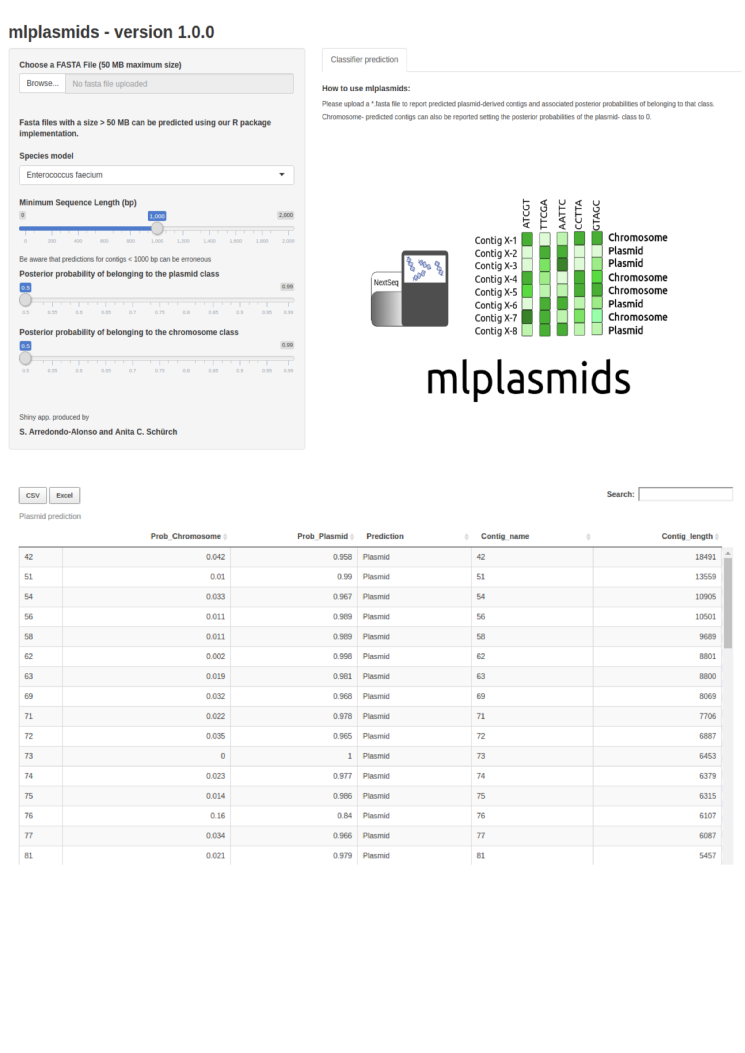
To use mlplamids with larger batches of genomes
Install and load the R package
install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_git("https://gitlab.com/sirarredondo/mlplasmids")
library(mlplasmids)
Load the fasta file containing the sequences into R
# Change the following object with the system location of your input file
my_path <- ('~/Data/E_faecium_plasmids/E745_control/E745_spades_contigs.fasta')
example_prediction <- plasmid_classification(path_input_file = my_path, species = 'Enterococcus faecium')
The value returned by the function is a dataframe that reports predicted plasmid-derived contigs.
head(example_prediction)
## Prob_Chromosome Prob_Plasmid Prediction
## 36 0.042683241 0.9573168 Plasmid
## 41 0.006876928 0.9931231 Plasmid
## 43 0.085699794 0.9143002 Plasmid
## 46 0.034722838 0.9652772 Plasmid
## 55 0.013318272 0.9866817 Plasmid
## 63 0.012378171 0.9876218 Plasmid
## Contig_name Contig_length
## 36 NODE_36_length_22926_cov_74.4686_ID_71 22926
## 41 NODE_41_length_19157_cov_27.6651_ID_81 19157
## 43 NODE_43_length_18357_cov_78.2779_ID_85 18357
## 46 NODE_46_length_16769_cov_25.6735_ID_91 16769
## 55 NODE_55_length_14069_cov_23.9568_ID_109 14069
Can we include other species in mlplasmids?
Yes! All the code that was used to train the models is available to generate ML classifiers for other species. We highly welcome pull requests to include additional species models into the package.
